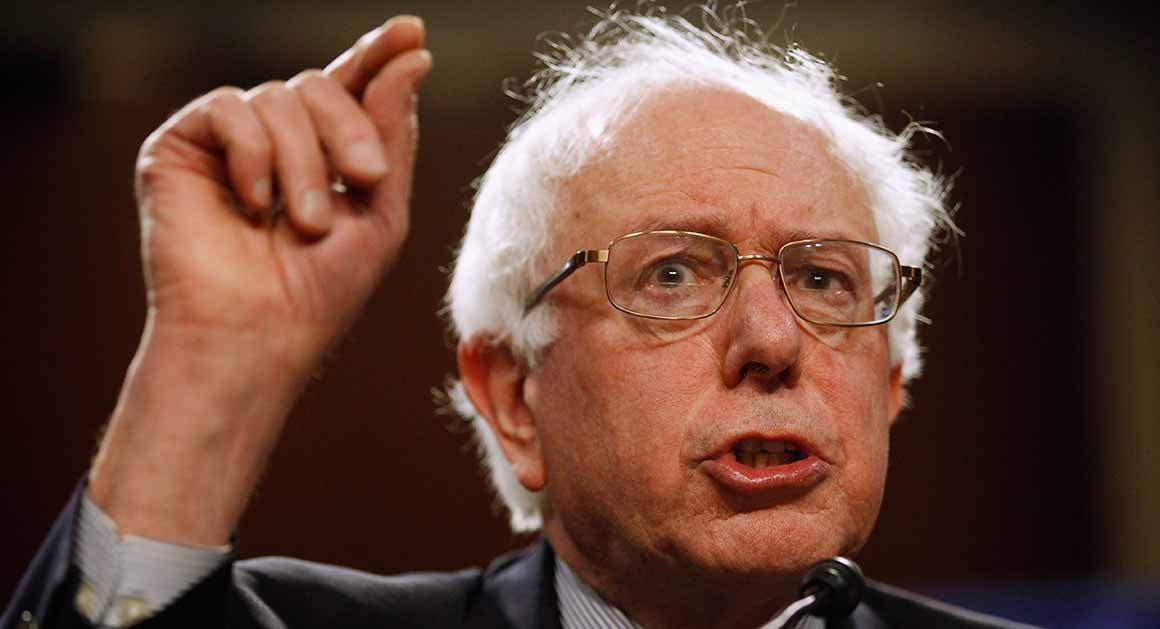

How can we interpret the incredible success of the “socialist” candidate Bernie Sanders in the US primaries? The Vermont senator is now ahead of Hillary Clinton among Democratic-leaning voters below the age of 50, and it’s only thanks to the older generation that Clinton has managed to stay ahead in the polls.
Because he is facing the Clinton machine, as well as the conservatism of mainstream media, Sanders might not win the race. But it has now been demonstrated that another Sanders – possibly younger and less white – could one day soon win the US presidential elections and change the face of the country. In many respects, we are witnessing the end of the politico-ideological cycle opened by the victory of Ronald Reagan at the 1980 elections.
Let’s glance back for an instant. From the 1930s until the 1970s, the US were at the forefront of an ambitious set of policies aiming to reduce social inequalities. Partly to avoid any resemblance with Old Europe, seen then as extremely unequal and contrary to the American democratic spirit, in the inter-war years the country invented a highly progressive income and estate tax and set up levels of fiscal progressiveness never used on our side of the Atlantic. From 1930 to 1980 – for half a century – the rate for the highest US income (over $1m per year) was on average 82%, with peaks of 91% from the 1940s to 1960s (from Roosevelt to Kennedy), and still as high as 70% during Reagan’s election in 1980.
This policy in no way affected the strong growth of the post-war American economy, doubtless because there is not much point in paying super-managers $10m when $1m will do. The estate tax, which was equally progressive with rates applicable to the largest fortunes in the range of 70% to 80% for decades (the rate has almost never exceeded 30% to 40% in Germany or France), greatly reduced the concentration of American capital, without the destruction and wars which Europe had to face.
In the 1930s, long before European countries followed through, the US also set up a federal minimum wage. In the late 1960s it was worth $10 an hour (in 2016 dollars), by far the highest of its time.
All this was carried through almost without unemployment, since both the level of productivity and the education system allowed it. This is also the time when the US finally put an end to the undemocratic legal racial discrimination still in place in the south, and launched new social policies.
All this change sparked a muscular opposition, particularly among the financial elites and the reactionary fringe of the white electorate. Humiliated in Vietnam, 1970s America was further concerned that the losers of the second world war (Germany and Japan in the lead) were catching up at top speed. The US also suffered from the oil crisis, inflation and under-indexation of tax schedules. Surfing the waves of all these frustrations, Reagan was elected in 1980 on a program aiming to restore a mythical capitalism said to have existed in the past.
The culmination of this new program was the tax reform of 1986, which ended half a century of a progressive tax system and lowered the rate applicable to the highest incomes to 28%.
Democrats never truly challenged this choice in the Clinton (1992-2000) and Obama (2008-2016) years, which stabilized the taxation rate at around 40% (two times lower than the average level for the period 1930 to 1980). This triggered an explosion of inequality coupled with incredibly high salaries for those who could get them, as well as a stagnation of revenues for most of America – all of which was accompanied by low growth (at a level still somewhat higher than Europe, mind you, as the old world was mired in other problems).
Reagan also decided to freeze the federal minimum wage level, which from 1980 was slowly but surely eroded by inflation (little more than $7 an hour in 2016, against nearly $11 in 1969). Again, this new political-ideological regime was barely mitigated by the Clinton and Obama years.
Sanders’ success today shows that much of America is tired of rising inequality and these so-called political changes, and intends to revive both a progressive agenda and the American tradition of egalitarianism. Hillary Clinton, who fought to the left of Barack Obama in 2008 on topics such as health insurance, appears today as if she is defending the status quo, just another heiress of the Reagan-Clinton-Obama political regime.
Sanders makes clear he wants to restore progressive taxation and a higher minimum wage ($15 an hour). To this he adds free healthcare and higher education in a country where inequality in access to education has reached unprecedented heights, highlighting a gulf standing between the lives of most Americans, and the soothing meritocratic speeches pronounced by the winners of the system.
Meanwhile, the Republican party sinks into a hyper-nationalist, anti-immigrant and anti-Islam discourse (even though Islam isn’t a great religious force in the country), and a limitless glorification of the fortune amassed by rich white people. The judges appointed under Reagan and Bush have lifted any legal limitation on the influence of private money in politics, which greatly complicates the task of candidates like Sanders.
However, new forms of political mobilization and crowdfunding can prevail and push America into a new political cycle. We are far from gloomy prophecies aboutthe end of history.
This piece was first published in Le Monde on 14 Febrary 2016

Expositores: Oscar Vidarte (PUCP) Fernando González Vigil (Universidad del Pacífico) Inscripciones aquí. Leer más
Una retrospectiva para entender los próximos cuatro años. Leer más
En la conferencia se hará una presentación de los temas más relevantes del proceso de negociación se llevó a cabo desde el 2012, así como del acuerdo de paz firmado entre el Gobierno colombiano y la guerrilla de las FARC a finales del 2016. Se analizarán los desafíos y las... Leer más
El Observatorio de las Relaciones Peruano-Norteamericanas (ORPN) de la Universidad del Pacífico es un programa encargado de analizar y difundir información relevante sobre la situación política, económica y social de Estados Unidos y analizar, desde una perspectiva multidisciplinaria, su efecto en las relaciones bilaterales con el Perú.
© 2026 Universidad del Pacífico - Departamento Académico de Humanidades. Todos los derechos reservados.

